MISSION DESIGN
SALTUS serves as the natural successor to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
by extending JWST's high-resolution observations of the interstellar medium into the far-infrared.
- SALTUS provides a powerful far-infrared (far-IR) space observatory to explore our cosmic origins.
- SALTUS is a pointed observatory in an L2 halo orbit and allows correlation of data with the JWST.
- It performs groundbreaking studies towards 1000s of astrophysical targets, including the first galaxies, protoplanetary disks, and various solar system objects over its 5-year baseline mission.
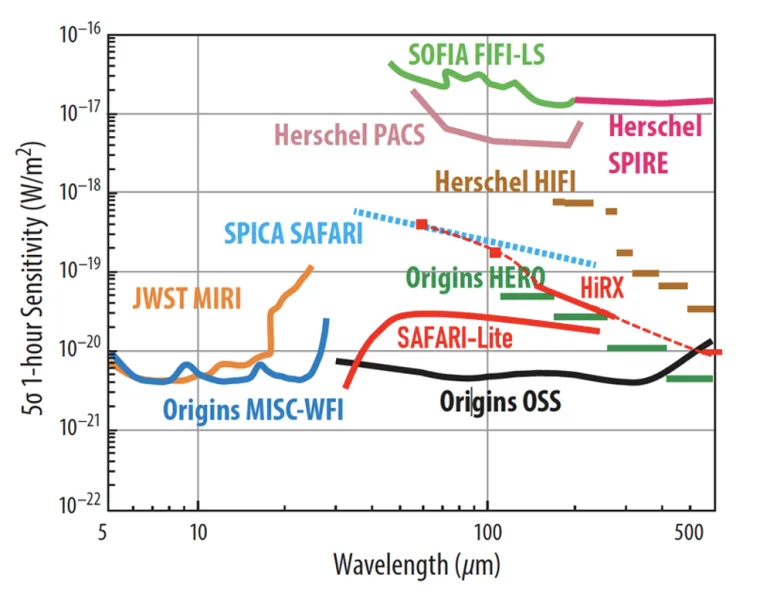
- SALTUS employs a deployable 14-m aperture, with a sunshield that radiatively cools the large off-axis primary to <45 K, along with cryogenic coherent and incoherent detectors that span wavelengths from 34 to 660 μm at high and moderate spectral resolutions
- SALTUS has 5x the collecting area of JWST and 16x that of Herschel, with a lifetime ≥5 years.
- >80% of SALTUS time is available for Guest Observers (GO).
- All SALTUS data will be made publicly available within 6 months of observation.
- With its large aperture and unique instrument suite, SALTUS bridges the knowledge gap between the local and distant universe, providing a quantum leap in the understanding of our cosmic origins
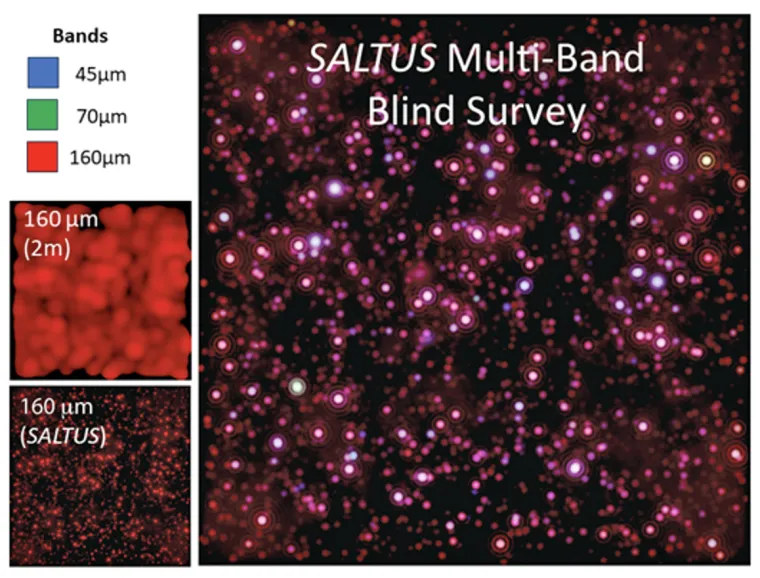
Large Aperture Provides High Sensitivity
Large Aperture Provides High Angular Resolution
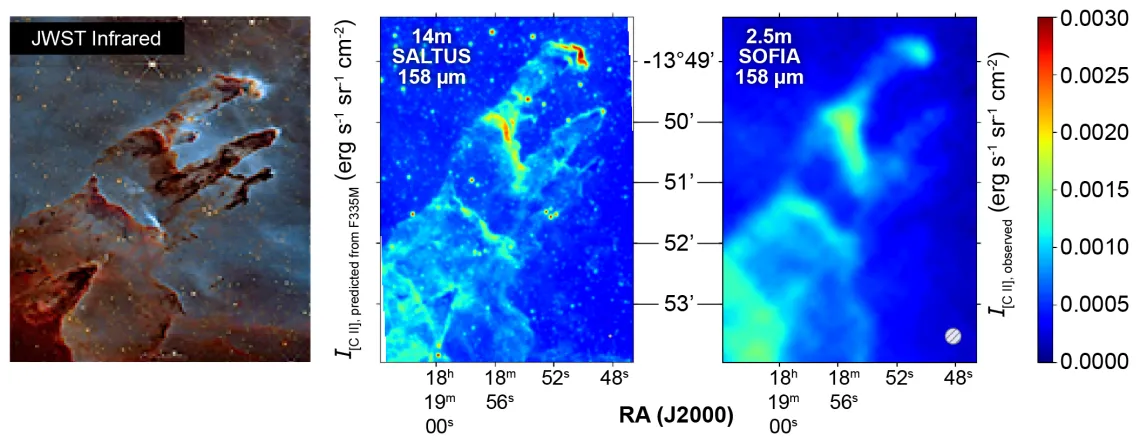
Simulated SALTUS image at 2.5" angular resolution (middle) of the [CII] 158µm emission in NGC 6611 (Pillars of Creation) is similar to the JWST image (left) and compared to a 2.5m reflecting telescope-created map (right). SAFARI-Lite can map this 10 arcmin2 region in 10 hours and simultaneously provide maps in all diagnostic lines of photo-dissociation regions (PDRs) and HII regions in our galaxy and the local group, probing the physical environment produced by radiation feedback of massive stars and its link to stellar clusters and its molecular core.
Large Aperture Provides Unbiased View of Distant Universe
SALTUS Achieves Full Sky Coverage
Similar to JWST, SALTUS can observe the entire sky in six months, while also providing two continuous 20º viewing zones around the ecliptic poles (animation generated for JWST simulating the instantaneous field of regard; credit J.Arenberg).